Smart City Application Use Cases and Software
Search and discover innovative IoT smart city applications and case studies as well as smart city Android and iOS apps for Amsterdam, NYC, London and Barcelona.
The following Channel Guide:
- Gives an overview of deployed Smart City IoT projects/products and the companies that have created them.
- Lists out a range of available smartphone apps for major cities and their features.
08/24/2021
Featured Provider
Nordsense
Nordsense Smart Waste Management uses artificial intelligence, machine learning and IoT, enabling cities to prevent bins from overflowing, and optimize routes to cut down on traffic congestion, fuel consumption, maintenance costs and carbon footprint
Smart City Vendors
Wearables / Citizen Data Sharing
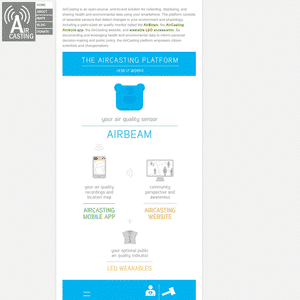
- TZOA
"TZOA uses internal sensors to measure your air quality, temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, ambient light and UV (sun) exposure all in one wearable device. "
Climate
- EverImpact
"We help Cities track their greenhouse gas emissions in realtime and monetize their reductions with Carbon Pricing Instruments."
Smart Street Lighting
Transportation
- BestMile
"BestMile offers an ecosystem to manage autonomous vehicle fleets: a fleet management software, a smartphone application, a system for traveler information and solutions for the control of smart infrastructure." - Kiunsys
"INES App, a product of Kiunsys, is full stack solution to deal with all aspects of parking including high level tools for management and analytics software down to street level occupation sensors and enforcing tools." - Anagog
"We collect and analyze in real-time raw signals from multiple smartphone sensors in order to determine and predict the user mobility status "
Smart Parking
- Streetline
- View our Smart Parking Guide here
Waste Management
- Enevo
- BigBelly
- Compology
- For a more complete list please visit our Smart Waste Roundup
Wastewater Management
Data Management
Data Visualization
- CityZenith
"The company's software platform maps and visualizes the torrent of data produced by modern cities to an intuitive real-time 3D simulation that anyone from the mayor to the engineer in the field can easily use." - G Element
- Solomon
"Solomon is a growing ecosystem of hyperlocal technologies, easily combined to create powerful tools and projects for use on the web."
Smart City Case Study Projects
Smartphone Apps

SMART CITY VADODARA
"Smart City Vadodara is an app which provides a platform to citizens of Vadodara to take part in Swachh Vadodara Mission (SVM) by complaining...
HUMAN APP
"Every day, people track over 3 million activities with Human. We keep track of daily activity in 900 cities all across the globe to learn about...

LOCALDATA
"LocalData is a cloud-based mapping platform that helps cities and communities make data-driven decisions by capturing and visualizing...
SENTILIO
"The main objective of the Sentilo platform is to provide a functional, open, interoperable, easily expandable platform for any city in the world...
General
Citizen Sensing
- Improve My City
"The application enables citizens to report local problems such as potholes, illegal trash dumping, faulty street lights, broken tiles on sidewalks, and illegal advertising boards. " - StreetBump
Pollution
Goods
Prototypes
City Initiatives
North America
USA
US Department of Transportation: Smart City Challenge
NYC
http://smartcitiesnyc.com/
San Diego
http://cleantechsandiego.org/smart-cities-home/
Chicago
http://www.cityofchicago.org/city/en/narr/foia/CityData.html
Canada
South America
Europe
- European Innovation Partnership on Smart Cities and Communities (EIP-SCC)
- Smart Cities Information System
- Civitas
Ireland
UK
Finland
Germany
Netherlands
Spain
-
-
- Barcelona: http://smartcity.bcn.cat/en
-
Asia
India
-
-
- Ministry of Urban Development | Smart Cities Mission
-
Singapore
UAE
Case Studies
A dive into some smart city projects in action
Array of Things
City Environmental Sensors
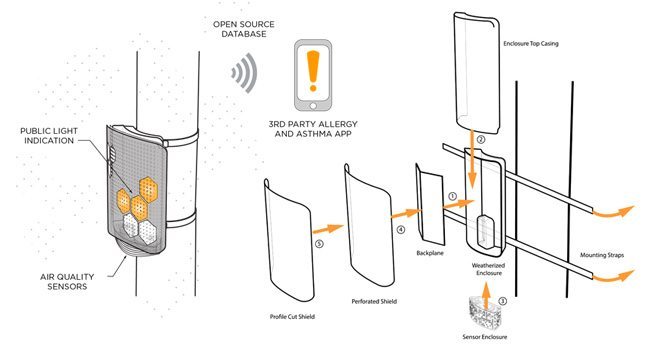
Created by researchers at Argonne National Laboratory and the University of Chicago, Array of Thingsis a network of sensor boxes that will be mounted to lampposts and other infrastructure around Chicago.
With the city government’s approval, each “node” in the network will collect block-by-block environmental data about temperature, humidity, light, air quality, and eventually even wind and precipitation. The nodes will also use a combination of noise levels, vibrations, and proximity detection of Bluetooth- and WiFi-enabled devices to get a rough measurement of vehicular and pedestrian traffic. Captured data will then be reported via cellular connectivity to an open database.
The researchers are quick to point out that no personal or identifying data will be collected in the process, and the entire project will go through multiple levels of public, academic and governmental review to make sure security and privacy are protected. The hardware and software are all open-source, and will be released on GitHub once the initial designs are finalized.

With the data the Array of Things generates, researchers, residents, city planners and other groups will have an unprecedented window into the life of Chicago’s urban environment. Weather forecasts could be improved based on the “microclimate” of specific neighborhoods. City managers could analyze traffic and weather patterns to better predict which streets need maintenance. Navigation apps could suggest more- or less-trafficked routes for both cars and pedestrians, or pick routes based on current air quality measurements.
Outside developers will be free to integrate the data into other apps, alongside the data already made available to them through the Chicago Data Portal that currently has 200 datasets and an API.
The first set of nodes will spend the winter on the Argonne National Laboratory and University of Chicago campuses for reliability testing. Researchers are working with the city on a pilot project agreement that would place additional nodes along Michigan Avenue in spring 2015, with the eventual goal of placing 500 or more nodes throughout the city by 2017.
Learn more at ArrayOfThings.github.io.

Strawberry Tree: Smart Public Spaces
Serbian startup Strawberry Energy makes solar charging installations for city parks, school and corporate campuses, and other public spaces. Its products provide renewable, off-the-grid energy in places that wouldn’t normally support device charging or wireless connectivity.
The Strawberry Tree is an angular, dendriform sculpture topped by a large, square solar panel. Sheltered below is a bench that doubles as a mobile charging station, offering a plethora of cords to suit any type of device. The installation also provides a WiFi hotspot and records environmental sensing data like temperature, humidity, and carbon dioxide and noise levels. With a large battery capacity that can provide thousands of quick charges (10 minutes or so) in the absence of sunlight, Strawberry Tree is designed to operate 24 hours a day, year round, no matter the weather.



Beyond its commitment to renewable energy, Strawberry takes the overall environmental lifecycle of its products into account. Strawberry Trees are built with recycled steel, and are designed to be easily disassembled so that 98 percent of the installation can be recycled or reused. This is especially important for the charging cords, which are clearly the most vulnerable part of the device to the stresses of weather and human misuse — Strawberry makes an effort to repair and refurbish damaged cords whenever possible, and they can be easily replaced.
Strawberry Trees and Minis have been in the wild for a few years now, mostly in Serbia, where they’ve reached more than 350,000 users. In April, the company received $125,000 from Bulgarian venture accelerator Eleven, and earlier this month it was a winner at the Verge Accelerate competition in San Francisco. In the wake of that success, Strawberry will continue to exhibit its technology in the U.S. and has begun negotiations to place Strawberry Trees in cities in California and other states.
Learn more at Senergy.rs

coolNYC
Community Smart Grid AC Control
At the intersection of the Internet of Things and the power industry is the smart grid — a 21st-century update to our electrical infrastructure that can link generation, demand, pricing and users in real time. Residents of New York City can get an early taste of this technology by joining the coolNYC program, which offers automation products and cash incentives to cut down on the use of air conditioners when the grid is straining under peak demand.
A collaboration between power supplier Con Edison and ThinkEco, an NYC startup that makes wirelessly-connected plugs and outlets — called “modlets” — that can turn appliances on and off through the Internet. The company’s smartAC kits add a remote thermostat, which senses the ambient air temperature in a room and communicates with a modlet hooked to the AC unit to keep the room at a desired temperature.
Residents who join coolNYC receive one of these smartAC kits free of charge, in exchange for allowing Con Edison to remotely lower the temperature or shut down the AC when there’s too much demand on the grid — typically for a few hours, and only on excessively hot days, which occur a few times each summer. Those who already own a Wi-Fi enabled AC unit (specifically the Friedrich Kühl and theFrigidaire Cool Connect) can also enroll in the program.

Folks who find other ways to beat the heat will be rewarded through a point system, which can be redeemed in the form of gift cards.
In addition to helping maintain the reliability of the city’s electrical grid, coolNYC participants get all of the benefits of a smart, Internet-connected AC unit: automatic temperature adjustments, remote control through the ThinkEco app, and a cloud-based dashboard to track energy reductions and savings that will be reflected in lower energy bills.
Check out the program at coolnycprogram.com, and watch the video below to learn more about ThinkEco.
Related: Smart AC Retrofits

Uber Spots
Uber expects to have a record night for its crowdsourced taxi service this New Year’s Eve, and in the run-up to the holiday the company has been testing a usability improvement that could make it easier for riders and drivers to find each other amidst the crowds of revelers.
Spot, which was rolled out in the Seattle area at the beginning of December, adds a color-coding feature to the Uber app. When making a pickup request, riders select their favorite hue from a basic color wheel. If the driver has a Spot device, which seems to be a wirelessly connected light strip placed along one side of the front windshield, it will glow appropriately when the car nears the pickup location. Users can signal back by lighting up their phone’s screen with the matching color.
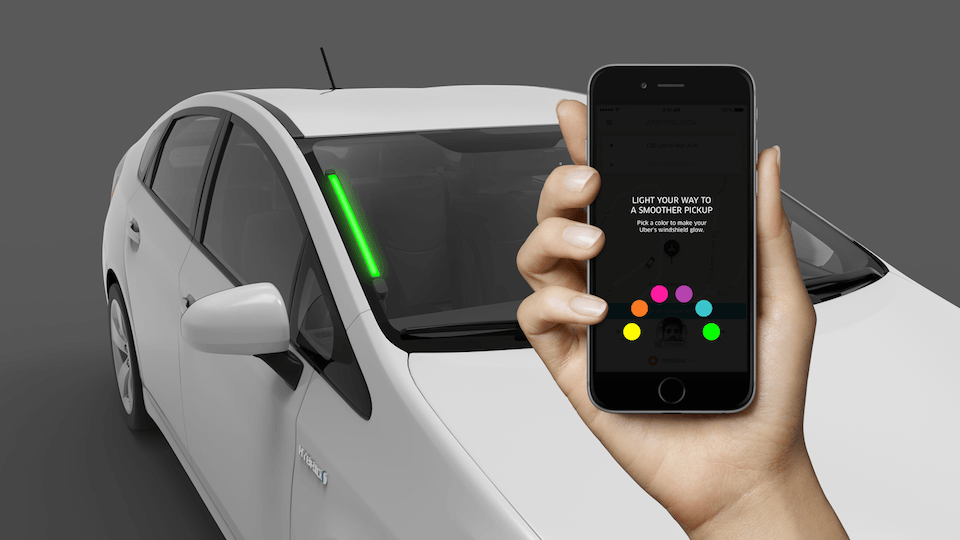
The new system isn’t foolproof — it’s unclear how Uber will ensure that people in the same pickup area don’t all choose the same color, for instance — but it’s a simple way to minimize the human error that is inevitably introduced when it comes time to find an unfamiliar car, at night, in the dark, through a crowd, while possibly inebriated. Spot is a reminder that a little bit of connected hardware can sometimes maneuver around a natural human roadblock in an otherwise app-driven process.
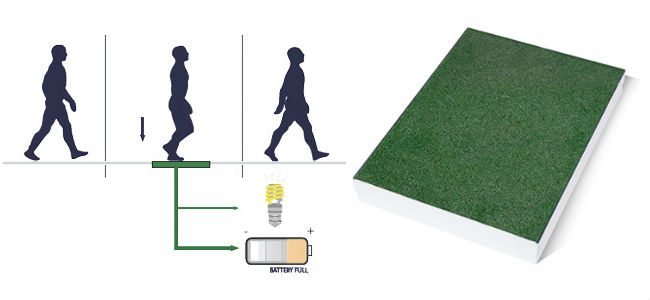

Pavegen: Smart Paving
Started by London based Laurence Kemball-Cook, Pavegen Systems is a company looking to provide cities with an alternative way to power some of their infrastructure using kinetic energy harvested from pedestrian footsteps.
Developed using at least 80% recycled materials the companies floor tiles will produce 4-8 joules (the equivalent of 8 Watt Hours) of energy when stepped on by a passer-by. 5% of that generated energy will be used to power the tiles built-in LED lighting and the remaining 95% will be stored in lithium cells for later use in lighting, signage or other low voltage applications located nearby.
The tile units also have integrated wireless technology and an API service as part of their feature set enabling information about the number of footfalls, traffic counts and total amount of energy generated for each tile to be transmitted to users for display/analysis from up to 200 meters away.
Being targeted for sales and installations in areas where other forms of renewable energy may be less effective CEO Kemble-Cook explains: “Pavegen’s is charting a newcourse for off-grid localised energy generation and smart grids. It’s quick and easy to install, and if used widely across areas of high footfall such as shopping malls, businesses and transportation hubs has the potential to have a dramatic effect on the UK’s long-term carbon emission levels.”


Soofa: Smart Urban Furniture
Consider the bench: an unassuming but iconic feature of urban landscapes. In the rush to make cities smart, what better place to begin?
Soofa, the first creation of MIT Media Lab spinoff Changing Environments, is a simple improvement on a simple seating arrangement. A self-contained, weatherproof solar charging station occupies some of the real estate, gathering enough energy for about 8 hours of charging time each day (or night) through two USB ports. Sensors in the bench will also record environmental data such as air quality and noise levels, which will be reported on Soofa.co.
Changing Environments’ co-founders — Sandra Richter, Nan Zhao and Jutta Friedrichs — say their goal is to “create an infrastructure for smart spaces tailored to the mobile generation.” The company was featured at the White House Maker Faire last summer.
Several industry partners are helping the company get started, including Verizon, whose 4G network the benches will use to send sensor data, and Cisco, which is funding the initial installation of a dozen benches around Boston. According to the company’s blog, the first
Soofa was placed in Boston Common in July and was in use within minutes.
Additional resources
Videos
- Good cities, not just smart cities | Daniele Quercia
- Conference Videos: Desiging Smart Cities: Opportunities and Regulatory Challenges | 3/31/2015
- FAB 10: Smart City States | Bruce Sterling | 7/15/2014
Background Articles
- The Street as Platform 2050 | Dan Hill | 5/24/2016
- IT Law Community: The Promise and Perils of Smart Cities | Rob Kitchin | 8/6/2015
- Guardian: We can’t allow the tech giants to rule smart cities | Paul Mason | 10/25/2015
- How We Get To Next: Give Us Smarter Cities, Block by Block | Scott Smith | 9/31/2015
-
Can Engineers Build Inclusive Smart Cities? | Dr. Anthony Townsend | 1/12/2015
-
Urban Omnibus: Against the Smart City | Adam Greenfield | 11/23/2013
- Open Knowldedge: Open Public Data: Then What? | Daniel Kaplan | 1/28/2011
Background Graphics
Blogs
- Smart & Resilient Cities
- Data Cities
- Jobs4Paki
- The Urban Technologist | Rick Robinson
Books
-
The Hackable City: A Research Manifesto and Design Toolkit | Cristina Ampatzidou, Matthijs Bouw, Froukje van de Klundert, Michiel de Lange, Martijn de Waal | 1/2016
- Smart Citizen, Smarter State | Beth Simone Noveck 11/2015
- The Responsive City | Stephen Goldsmith and Susan Crawford | 9/2014
- Smart Cities: Big Data, Civic Hackers, and the Quest for a New Utopia | Anthony Townsend | 10/7/2013
General Resources
- Global Smart City and Community Coalition - GSC3
- New Urban Mechanics
- City Protocol
"The goal of City Protocol is to define an interoperable city platform, which will allow cities to communicate and operate across silos and across communities, spawning an ecosystem of solution development and innovation." - Metrolab